Case Study – Design Vision
The following is an excerpt from the Delft Design Guide.
Daalhuizen, Jaap. 2018. Delft Design Approach, Delft University of Technology.
Design Vision
Function
The most important functions for the design are:
- Transport children on water, the toy needs to float on water, the transportation function enables that children can take part in competitions and water cycle
- Transform muscle strength into driving force; the children have to use of the driving mechanism to move the water cycle
- Teach children something about mechanics; one of the goals of the company is to introduce children to mechanics and how the product works
- Children should enjoy themselves; of course this has to be a result of the points listed above
Target Group
The most important target group are children from 7 – 11 years. Nevertheless the product also needs to be used by youngsters and elder people. A distinctive characteristics of this group is the ability to swim thus need less guarding. Children have a lot of fantasy and have a keen interest in mechanics. The other relevant group is camping users or café users next to lakes. The intention is that these people buy the product to provide children with maximum fun. These people do not care about the product. They only want that it is stored very well during winter at minimum maintenance.
Interested Party
The remaining interested party are the parents. They want their child to have fun and at the same time be safe without their constant guard. Others concerned are other water users who should experience minimum inconvenience from the product, the water cycle.
Environment for use
The product is going to be used on lakes next to campings and other recreational areas. Lakes have no current, often little beaches with gras on them. Lakes often have little cafes or toilet spots which could serve as storage space for the product.
Relation with other products
The product will have to compete with other water game activities. Other products can be water cycles, beach balls but also bigger beach balls or rubber boats. The unique quality of this product is that it embodies all of these functions including the fantasy aspect of the target group.
Distinguishing aspects
The product needs to command attention in between all other activities in such a lake. It has to come across as very safe. The product needs to be produced as environmentally friendly as possible and should resist long term influences of sand, water and sunlight.

How do we set our Design Goals or Vision?
The following is an excerpt from the Delft Design Guide.
Daalhuizen, Jaap. 2018. Delft Design Approach, Delft University of Technology.
What Is a Strategy Wheel?
A strategy wheel is a visual representation and a quick tool to review a company’s strengths (see figure 2.1). A strategy wheel presents the company’s competencies on the axes, and the scores of the competencies on those axes. By using the diagram, you obtain a quick understanding of the company’s strategic strengths. Often it is useful to construct strategy wheels of a company’s direct competitors. A product innovation process (see section 1.2 in the PDF linked above) starts with a clear understanding of the current situation of a company. The need for a new product arises from an understanding of a company’s strategic strengths and weaknesses, and the opportunities in the market. A thorough analysis of the current situation of a company yields an understanding of the company’s strategic strengths (for example: technical know-how, product portfolio, development (capability), financial position, export know-how, marketing, organization and personnel, management). The strategy wheel is sometimes used to compare other things than a company’s strategic position. For example, design concepts can be analyzed and reviewed using the strategy wheel (see fig. 2.1). The axes represent design requirements on which the design concepts are evaluated. The strategy wheel then yields a visual representation of the scores of the different design concepts on the design requirements. Also, there are various adaptations of the strategy wheel (for example the ‘EcoDesign Strategy Wheel’, in this section).
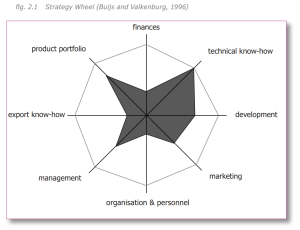
When Do You Use a Strategy Wheel?
A strategy wheel is usually applied in the beginning of a new product development process in order to present the strategic strengths of a company.
How to Use a Strategy Wheel?
Starting Point The results of an internal analysis form the starting point for the use of the strategy wheel: a clear understanding of the company’s strategic strengths in relation to its direct competitors. Expected Outcome The outcome of the use of the strategy wheel is a visual representation and a better understanding of the company’s strategic strengths.
For an example of using a strategy wheel see: The Strategy Wheel (The Big Picture View of How You Will Win)

